(+86)0532-88988868
In developed countries, the vast majority of water plants use specialized water treatment salts as consumables for the operation of sodium hypochlorite generators. Equipment suppliers, taking a leading European industry brand as an example, provide specialized electrolytic salts as standard equipment for their tap water disinfection equipment deployment in developed countries. In China, the online preparation of sodium hypochlorite system still widely uses self purchased ordinary iodine free edible salt as a consumable.
However, the national standard GB/T5461 for edible salt does not provide applicability explanations for the application environment of water treatment; The trace bromine components in edible salt can produce toxic carcinogens under electrolysis, which affects the safety of tap water quality; The anti fouling agent in edible salt can produce by-products such as trivalent iron during the electrolysis process, which affects the stable operation and lifespan of the equipment and increases maintenance costs. The use of salt for water treatment has been strictly controlled for a series of trace elements related to electrolysis applications, and the industry behavior of replacing salt for water treatment with edible salt is temporarily in the national regulatory gap.
Edible salt cannot replace salt used for water treatment
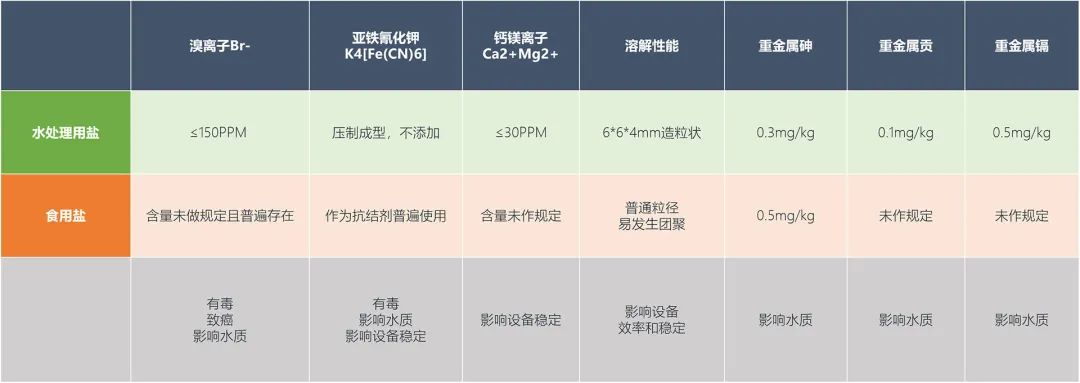
The impact of the above indicators on the hygiene indicators of drinking water:
1. Bromine ion Br - forms bromate through electrolysis, and bromate is recognized by international organizations as a potential carcinogen! When the bromine ion content in the disinfectant salt is ≤ 150PPM, the bromate ion content originating from the disinfectant salt can be controlled at 0.001 PPM, which is much lower than the national standard GB5749 sanitary standard for domestic water, the bromate ion content index of 0.01 PPM.
2. Potassium ferrocyanide K4 [Fe (CN) 6] is commonly used as an anti caking agent in edible salt. Potassium ferrocyanide produces toxic substance potassium ferrocyanide under electrolysis, which can cause kidney damage; At the same time, under ultraviolet or light irradiation, heating or acid action, further hydrocyanic acid (HCN) will be generated, which is toxic; Under high temperature burning, it will completely decompose into highly toxic potassium cyanide. The national standard GB5749 specifies that the standard for iron ion Fe+in domestic water is ≤ 0.3PPM, and the introduction of potassium ferrocyanide will also increase the content of iron ions in the water; And under the action of electrolysis, ferrocyanide precipitates will be generated, affecting water quality and chromaticity.
3. The national standard GB5749 specifies the content of lead, arsenic, mercury, cadmium, and barium in heavy metals as follows: lead 0.01mg/L, arsenic 0.01mg/L, mercury 0.001mg/L, cadmium 0.005mg/L, and barium N/A. The natural "low" heavy metal content in salt used for water treatment will provide a more perfect heavy metal indicator for drinking water.

The impact of the above indicators on the operation of sodium hypochlorite generating equipment:
1. The Fe3O4 generated by the electrolysis of potassium ferrocyanide carries the risk of piercing or blocking the diaphragm for a diaphragm generator; For non diaphragm generators, increasing energy consumption carries the risk of producing excess by-products.
The introduction of calcium and magnesium ions into the salt not only increases the electricity consumption of the sodium hypochlorite generator electrolysis, but also forms scaling phenomenon, affecting the stable operation of the generator. The stable operation of the generator can ensure the stability of disinfection in water purification enterprises and ensure the safety of water use for thousands of households.
3. Ordinary sized table salt will form a relatively stable layer of salt blocks at the bottom of the water, making it difficult to completely dissolve. It may also be easy to produce supersaturated solutions, where crystals are not completely melted and suspended in the solution, but are sucked into the electrolysis equipment. This non liquid crystal cannot be electrolyzed, causing waste, and in severe cases, it can lead to poor operation of the generator. The form of salt granulation used for water treatment can avoid the problem of agglomeration during transportation and storage without the addition of potassium ferrocyanide (anti caking agent); At the same time, the large gaps between particles are conducive to water penetration, facilitate uniform and rapid dissolution, and help to form a stable saturated solution, maintaining the good operation of the equipment.

Comply with policy norms and industry standards:
The industry standard for salt used in water treatment has been formulated and promulgated by relevant institutions designated by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, which plays a normative role in the use of salt in the water treatment industry;
Reduce by-products and meet the requirements for improving water quality:
Compared to edible salt, salt used for water treatment meets the highest standard technical indicators in terms of bromine ion and heavy metal content, preventing the occurrence of "active poisoning" caused by substandard indicators in water plant production, and meeting the requirements of local governments, especially densely populated cities, for upgrading water quality standards.
Beneficial for equipment maintenance and reducing maintenance costs:
Compared to edible salt, salt for water treatment has strict regulations on its calcium and magnesium ion content, potassium ferrocyanide content, and solubility, which is conducive to the stable operation of equipment and reduces the cost of daily maintenance.
(Source | New Horizon of Water Treatment)


